Introduction
Medical science is advancing at an unprecedented pace, bringing innovations that are transforming the way diseases are diagnosed, treated, and prevented. From gene therapies and AI-driven diagnostics to breakthrough treatments for chronic conditions, 2025 has delivered medical breakthroughs that are reshaping healthcare. This article explores the top 10 recent medical breakthroughs, highlighting their impact on patient care and the future of medicine.
1. Gene Therapy Cures for Sickle Cell and Genetic Disorders
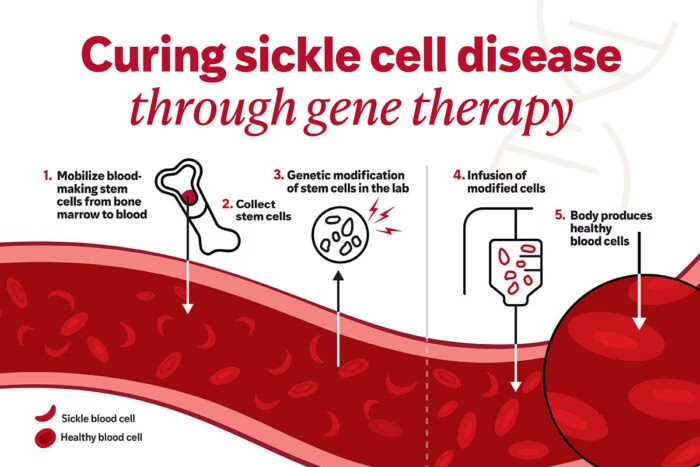
Gene therapy reached a historic milestone with one‑time curative treatments for previously traumatic chronic illnesses. 2025 has seen two major gene therapies, Casgevy and Lyfgenia, approved to treat sickle cell disease (SCD), where patients’ hemoglobin is defective due to a genetic mutation. These therapies use cutting‑edge CRISPR‑based and lentiviral vector editing to enable healthy hemoglobin production, effectively preventing painful crises characteristic of SCD. The regulatory approvals mark the first time CRISPR‑edited therapies have been cleared for clinical use, opening a door to curing inherited disorders that were previously managed symptomatically.
For millions worldwide affected by sickle cell disease, gene editing promises a lifelong cure rather than chronic treatment. Health systems can focus resources on prevention and rehabilitation instead of recurring hospitalizations. Moreover, this success paves the way for future therapy in other genetic conditions like β‑thalassemia and rare metabolic disorders, democratizing a new era of genomic medicine.
2. Twice‑Yearly HIV Prevention That Changes the Game

In 2025, health agencies globally recognized lenacapavir (Yeztugo®) as the first injectable pre‑exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV that only requires two doses per year. This formulation simplifies longstanding prevention regimens requiring daily pills, which have historically suffered from adherence challenges. Clinical data show lenacapavir maintains nearly 99.9 percent efficacy in preventing HIV transmission, vastly outperforming traditional strategies.
Biannual injections could be transformative for regions with high incidence rates, particularly in sub‑Saharan Africa, where healthcare access barriers have limited PrEP uptake. Simplified delivery models make prevention more equitable and accessible, driving down infection rates and turning HIV prevention into a global success story.
3. Needle‑Free Emergency Allergy Treatment

Food allergies and anaphylaxis can be life‑threatening, with epinephrine injection being the immediate first line of defense. However, needle phobia and technical challenges often delay administration. In 2025, Neffy, the first FDA‑approved nasal epinephrine spray, emerged as an alternative to traditional auto‑injectors. This delivery method uses an innovative absorption enhancer to maintain rapid blood uptake without needles.
By eliminating needles, Neffy empowers caregivers and patients to respond to allergic emergencies quickly and confidently. Schools, workplaces, and homes equipped with nasal epinephrine add an extra layer of lifesaving readiness. It also expands access where training and administration of shooter devices may be limited.
4. Non‑Opioid Pain Relief for Acute Conditions

Opioid dependence remains a critical public health issue. In response, suzetrigine (marketed as Journavx) was approved in 2025 as a novel non‑opioid oral pain medication. Rather than interacting with central opioid receptors, this compound targets peripheral sodium channels (Na_V1.8), halting pain signals without risk of addiction or respiratory depression.
For postsurgical and acute injury management, reliable non‑opioid alternatives offer effective analgesia while reducing the risk of opioid misuse. Journavx represents a pivotal step toward pain relief strategies that are both safe and clinically effective, benefiting patients and public health.
5. AI‑Enhanced Diagnostics in Disease Detection

Artificial Intelligence (AI) integration into diagnostics has ushered in a new medical frontier. Deep learning models now enable early detection of complex diseases, even before symptoms manifest. For instance, recent developments highlight AI‑driven diagnostic systems approved for identifying heart disease, brain tumors, skin cancer, and lung disease with high accuracy, enhancing clinical confidence and patient outcomes.
Moreover, AI models like AlphaFold 3 now predict protein structures accurately, accelerating early drug discovery and shortening development cycles. Researchers leverage AI to analyze massive genomic and imaging datasets, identifying subtle patterns that human clinicians may overlook.
AI’s integration into diagnostic workflows helps reduce misdiagnosis, facilitates personalized care plans, and improves early intervention success. As AI tools mature, clinicians will increasingly have data‑driven insights, making healthcare faster, more precise, and more equitable.
6. Breakthroughs in Early Cancer Detection and Treatment

Cancer research remains at the forefront of medical breakthroughs. One standout innovation is a hybrid imaging technology designed to detect cancer and other diseases with unprecedented precision, funded by the NIH and currently progressing toward clinical validation.
Meanwhile, regulatory expansions for therapies such as 177Lu‑PSMA‑617 (Pluvicto ®) for metastatic prostate cancer exemplify targeted radioligand treatment strategies that attach to cancer‑specific proteins, significantly improving outcomes for advanced disease cases.
Global efforts to combat cancer also include immunotherapy innovations, including gamma delta T‑cell therapies that recognize stress signals on tumor cells and personalized pharmacogenomic prescribing that tailors antineoplastic drugs to individual genetic profiles.
These developments contribute to a multi‑pronged fight against cancer that increases therapeutic success while minimizing side effects and expanding individualized care.
7. Stroke Treatment Innovations

Stroke is a leading cause of long‑term disability worldwide; thus, innovations in acute treatment can dramatically improve outcomes. India made headlines in 2025 with its first indigenously designed Supernova stent retriever, showing exceptional results in clinical trials led by AIIMS New Delhi, restoring brain blood flow in severe stroke patients with very high efficacy.
What makes this innovation notable is that it achieves outcomes comparable to global standards while remaining cost‑effective. With regulatory approval and widespread deployment, this device stands to save many lives across regions where access to cutting‑edge technologies has historically been limited.
8. Early Pancreatic Cancer Detection via Breath Biomarkers
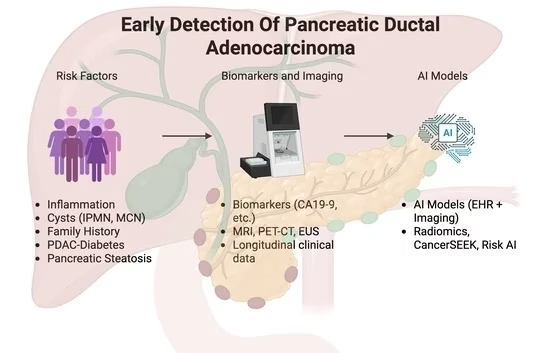
Pancreatic cancer typically presents late and carries a poor prognosis. In late 2025, results began emerging from clinical studies like the VAPOR study in the UK, where researchers used breath analysis to detect volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with pancreatic cancer signatures. This approach could revolutionize early detection, improving survival prospects dramatically if clinical validity holds.
Transitioning from symptom‑based diagnosis to non‑invasive breath analysis could transform how pancreatic cancer—and potentially other cancers—is screened in high‑risk populations. Early detection is strongly correlated with increased survival, making this a high‑impact breakthrough.
9. Brain‑Computer Interfaces Restoring Function

Brain‑computer interfaces (BCIs) are no longer conceptual technologies; in 2025, progress in clinical applications has enabled patients with paralysis to control digital devices using thought alone. For example, a patient in the UK using a Neuralink implant controlled a computer merely hours after implantation, demonstrating real‑world potential to restore communication and autonomy to individuals with severe motor impairments.
BCIs hold promise beyond rehabilitation—they could assist in sensory restoration, cognitive augmentation, and personalized neurotherapy. As safety and usability improve, these technologies may become mainstream tools for treating neurological disorders.
10. Multi‑Target Precision Approaches to Alzheimer’s
Alzheimer’s disease remains one of medicine’s most elusive challenges. Historically, treatments targeted amyloid plaques but with limited benefit for many patients. In 2025, researchers shifted toward multi‑target therapy models that combine agents addressing amyloid, tau proteins, inflammatory pathways, and other underlying biological mechanisms simultaneously.
By employing precision medicine concepts rooted in oncology, Alzheimer’s trials are now identifying subgroups of patients who respond best to specific combinations of therapies. This personalized approach increases the likelihood of slowing or modifying disease progression, offering hope to millions worldwide.
Conclusion:
2025 is shaping up to be one of the most transformative years in recent medical history. From genetic cures to AI‑enabled diagnostics, from needle‑free emergency care to thought‑controlled interfaces, these breakthroughs redefine what is medically possible. Each advancement not only solves specific clinical problems but also contributes to a more responsive, equitable, and personalized healthcare system.
As these innovations continue to mature through research, regulatory approval, and clinical use, their collective impact will improve millions of lives worldwide—shaping a healthier, more resilient future.
Read more trending HEALTH news here.
![]()