Introduction
In 2026, smart home technology has evolved from a luxury niche into an essential component of modern living. What was once a futuristic idea—homes that anticipate needs and adjust environments automatically—has become reality for an ever‑growing number of households. From enhanced security and seamless connectivity to energy optimization and AI‑driven automation, the integration of smart features is transforming how we live, interact, and design our homes. Across all categories, homeowners are prioritizing convenience, safety, sustainability, and aesthetic integration without visual clutter in their spaces.
This comprehensive article explores the Top 10 Smart Home Features in Modern Design, blending current trends and recent industry developments. It is written to be engaging, realistic, and optimized for search engines: rich with keywords, transition phrases, authoritative links, and relevant examples.
1. AI‑Powered Home Automation

Smart homes in 2025 and 2026 increasingly rely on artificial intelligence (AI) to deliver anticipatory automation. Unlike traditional systems that respond only to direct commands, modern AI‑driven homes analyze patterns in daily behavior, occupancy, and environmental conditions, allowing them to act proactively. In practical terms, AI can adjust lighting and thermostats according to your schedule and habits, optimize energy usage by learning daily routines, and even predict appliance needs—for example, suggesting recipes based on the inventory in your pantry. This level of intelligent automation transforms the home into a responsive, adaptive environment that enhances convenience, efficiency, and comfort.
AI automation goes beyond simple “rule‑based” routines. According to recent market observations, AI‑driven home systems are now capable of predictive behavior and decision‑making—for instance, adjusting temperature settings based on both the homeowner’s routine and local weather forecasts, or suggesting energy‑saving tips based on usage data.
Samsung’s expanding lineup of Bespoke AI appliances—refrigerators, washers, and more—show how AI is embedded directly into household equipment for smarter daily control.
Together with increasingly powerful central hubs, AI automation will continue to define what it means to live in a truly smart home.
2. Voice and Conversational Controls

Another foundational trend in smart home design is the expanded use of voice and conversational controls. Voice interfaces such as Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple Siri (via HomeKit) have become pervasive—integrated into smart speakers, dedicated displays, mirrors, and even kitchen appliances.
Recent device launches underscore this trend. For example, Amazon’s Echo Show 11 and Echo Show 8 (fourth generation) include next‑generation voice processing capabilities and larger displays to serve as intuitive command centers for the smart home.
Voice control remains essential because it enables hands‑free interaction for individuals managing multiple tasks, provides accessibility for users who prefer not to rely on mobile apps, and seamlessly scales across devices ranging from lighting and entertainment systems to climate control. By offering a natural and intuitive interface, voice control enhances convenience, improves efficiency, and ensures that smart home technology is accessible to a wide range of users.
In combination with enhanced natural language processing and AI learning, voice control is rapidly becoming the default interface for smart homes.
3. Matter and Interoperability Standards

One of the most impactful technological shifts in recent years has been the emergence of the Matter standard. As a unified connectivity protocol, Matter enables devices from different manufacturers—whether Apple, Google, Amazon, or others—to communicate seamlessly. It eliminates the historical fragmentation and compatibility barriers that once required homeowners to juggle multiple hubs or proprietary apps.
Support for Matter is expanding rapidly. For instance, Aqara has added support for more than 50 new Matter device types, enhancing cross‑platform interoperability and automation.
The Matter standard matters because it enables single ecosystem control through voice commands, mobile apps, or centralized dashboards, simplifying the management of smart home devices. It also reduces setup complexity in multi‑brand environments, allowing devices from different manufacturers to work seamlessly together. Additionally, Matter provides a future‑proof foundation for emerging innovations, ensuring that new devices and technologies can integrate smoothly into the smart home ecosystem without compatibility issues.
With interoperability growing ever more robust, integration issues are diminishing—empowering users to buy smart devices freely rather than being locked into one brand ecosystem.
4. Integrated Smart Security

Security continues to be a top priority for smart home adopters. Today’s integrated systems go far beyond wired alarms and basic motion detectors—they use AI‑enhanced surveillance, biometric access, and predictive alerts that protect properties in real time.
Key features in modern smart home security include smart doorbells with enhanced motion detection zones and package recognition, facial recognition and AI‑driven event filtering to reduce false alarms, and smart locks offering biometric access and Ultra‑Wideband (UWB) proximity unlocking for seamless entry. These systems are further strengthened by centralized dashboards that unify alerts from cameras, sensors, locks, and alarms, providing homeowners with a comprehensive, real‑time overview of their property’s security.
According to recent analysis of smart home trends, security systems are becoming more predictive and customizable, using AI to identify unusual patterns rather than simply trigger alerts after events.
These systems are optimized for modern lifestyles and frequently integrate with home automation routines—for instance, locking doors automatically when a homeowner leaves and activating cameras at night.
5. Smart Energy and Climate Management
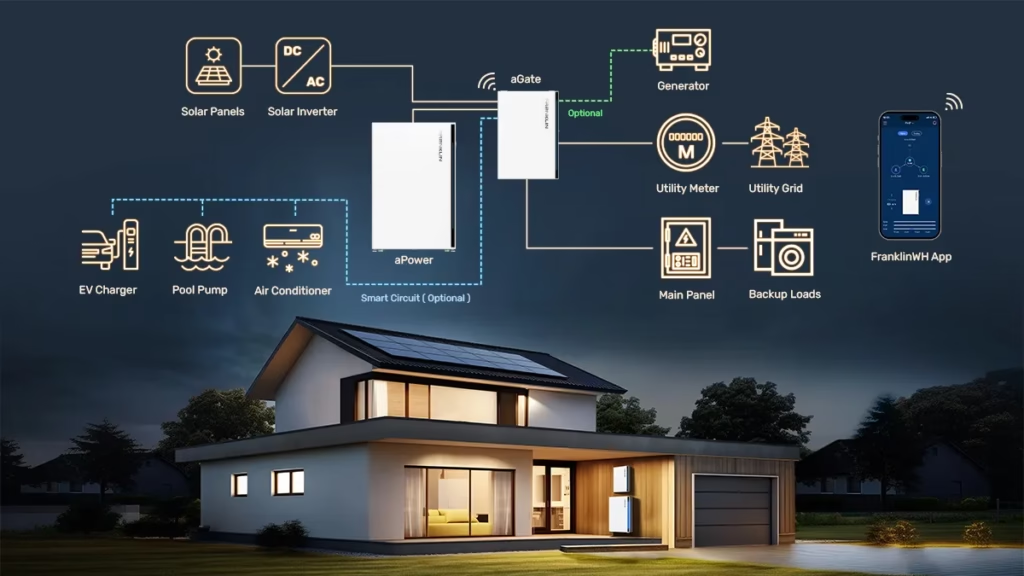
With sustainability high on the agenda for both consumers and policymakers, smart homes are now central to energy efficiency and climate control. Smart thermostats, sensors, and integrated systems help manage consumption, reduce waste, and lower monthly utility costs.
This shift aligns with broader trends in sustainable living, as technologies like solar integration and whole‑home energy storage become increasingly mainstream. Modern energy systems now provide real-time monitoring of electricity usage, automated adjustments based on occupancy and weather forecasts, seamless integration with solar panels and home battery systems, and demand response support to reduce strain during peak usage. Together, these features enhance energy efficiency, lower costs, and support environmentally responsible living.
Recent insights show that smart energy systems are not only about convenience, but also significant long‑term financial savings and environmental benefits.
These capabilities make smart climate control one of the most valuable features in modern homes—especially in regions with variable electricity pricing or environmental regulations.
6. Smart Lighting and Aesthetics

In modern design, technology must not only be functional but visually integrated. Smart lighting systems have evolved from simple color‑changing bulbs to dynamic, tunable lighting that adjusts throughout the day to support comfort, mood, and even wellness.
According to smart home design forecasts, tunable lighting—which can shift between warm and cool tones to mimic natural circadian rhythms—is among the top innovations driving smart home adoption. Key lighting innovations include circadian lighting systems that support sleep and productivity, scene creation where lights automatically adjust based on specific activities such as reading or entertaining, and invisible or integrated fixtures that blend seamlessly with architectural design. These advancements not only enhance functionality but also contribute to the aesthetic and wellness aspects of modern homes.
From ambience‑setting for everyday use to health‑oriented lighting strategies, smart lighting enhances both design aesthetics and human experience.
7. Health and Environmental Monitoring

Another burgeoning area of smart home technology is health and environmental monitoring. Modern systems monitor air quality, humidity, noise levels, UV exposure, and even biometric data to create healthier living environments.
Many devices now integrate seamlessly with home automation routines, allowing the home environment to respond intelligently to changing conditions. For example, air purifiers can automatically adjust on days when outdoor air quality is poor, HVAC systems maintain optimal humidity levels recommended for respiratory health, and lighting adapts to sleep-cycle optimization programs to support better rest and overall wellbeing. This level of integration helps create healthier, more responsive living spaces with minimal manual intervention.
Smart environmental technologies are especially relevant for families, elderly residents, or anyone concerned about indoor air pollutants and overall wellbeing. These systems are frequently part of broader “wellness‑oriented living spaces,” a recognized growth area in smart home trends.
8. High‑Speed Networking Infrastructure

Connectivity is the backbone of any smart home—and with ever‑growing numbers of connected devices, traditional Wi‑Fi is no longer sufficient. Wi‑Fi 7 and advanced mesh networking solutions are emerging as the standards required to keep today’s homes responsive and reliable.
Wi-Fi 7 delivers multi-gigabit throughput and significantly reduced latency, providing the speed and responsiveness required for modern smart homes. When combined with mesh networking systems, uniform and reliable connectivity is ensured across large or multi-story homes. Additionally, integrated networking equipment supports IoT devices with priority bandwidth, allowing critical smart home functions to operate smoothly without disruption from high-demand applications such as streaming or gaming.
Robust network infrastructure isn’t just desirable—it is essential for reliable device communication, video streaming, AI processing, and real‑time automation.
9. Smart Robotics and Autonomous Devices

The next wave of smart home innovation involves robotic assistants that accomplish tasks ranging from cleaning to monitoring. While robot vacuums and mops have been popular for years, the latest generation introduces advanced AI navigation, object recognition, and even multi‑purpose functionality.
In 2025, autonomous devices began to demonstrate advanced capabilities that significantly improved their efficiency and usability. These devices are now able to learn home layouts and optimize cleaning patterns, identify obstacles such as cords, pet waste, or clutter, and operate self-maintaining base stations that automatically empty debris and wash mop pads. As a result, smart robotics have become more reliable, hands-free, and practical for everyday household use.
Future robotic systems are expected to expand beyond cleaning into areas such as surveillance, delivery of items within the home, and health monitoring.
10. Seamless Control Hubs and Dashboards

Finally, as smart home systems grow more complex, unified control hubs and dashboards have become indispensable. Rather than managing separate apps for lighting, climate, security, and entertainment, centralized dashboards unify these systems into a single interface—whether on your phone, tablet, wall‑mounted panel, or smart display.
This centralization significantly improves the ease of use within multi-device ecosystems by allowing all smart home functions to be managed from a single interface. It also enhances accessibility for all household members, regardless of technical proficiency, and enables deeper personalization of routines and scenes to match individual preferences and daily lifestyles.
Platforms that support cross‑brand integration (thanks to Matter and open APIs) are rapidly becoming the norm in modern smart homes.
Conclusion
The evolution of smart home technology in 2025–2026 is more than incremental; it represents an inflection point where design, sustainability, security, and intelligent automation converge. From AI‑driven behaviors to health‑focused systems and robust networking, modern smart homes are transforming everyday living into adaptive, personalized experiences.
As integration standards like Matter mature, and as device ecosystems become more interoperable, smart home adoption will continue its trajectory toward ubiquity. Whether you are retrofitting a single room or designing an entire smart home from the ground up, these top features provide a roadmap for both practicality and future readiness.
Click here to explore the latest trending news in home design and living.
![]()



